Since its invention by Tim Berners-Lee in the early 1990s, the internet has undergone radical change and has become an integral part of everyday life. This digital evolution has gone through several phases – from Web1 to Web2 to the emerging Web3.
Web 1.0: The birth of the World Wide Web
The earliest days of the internet, often referred to as Web 1.0, were characterized by static websites that offered little to no interactivity. Users could access information, but not react to it or change it. In this era, websites mainly served as digital brochures. The web was a one-way means of communication that thrived on its novelty. The basic building blocks – HTML for the structure of web pages, URLs for addressing and HTTP for transmission – laid the foundation for what the internet is today.
Web 2.0: The social and interactive web
With the advent of Web 2.0 in the early 2000s, the internet experienced a real paradigm shift towards interactivity, social networking and user-generated content. This shift was driven by the development of new technologies and standards such as AJAX and RSS, which enabled a more dynamic and interactive user experience. Platforms such as Facebook, Twitter and YouTube fundamentally changed the way people communicate and share content. The internet became a global meeting place that enabled everyone to be not only a consumer but also a producer of content. This era is characterized by the democratization of information dissemination and unprecedented networking.
The transition: Web 2.5
As the technology evolved, Web2 platforms began to integrate elements of Web3, leading to a hybrid phase often referred to as Web 2.5. This phase is characterized by a gradual approach to decentralized technologies without end users necessarily knowing that they are interacting with such technologies. It is a time of experimentation and adaptation, where traditional internet companies are beginning to explore the benefits of blockchain, artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve and future-proof their services.
Web3: The future of the decentralized Internet
Web3 represents the next stage in the development of the internet, based on the principles of decentralization, transparency and user control. Unlike its predecessors, which were dominated by centralized entities, Web3 aims to put the power back into the hands of the users. Through the use of blockchain technology, smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), Web3 enables online transactions and interactions to take place without the need for a trusted third party. This could lead to a radical transformation of many industries, from finance to media, by creating a more secure, transparent and efficient way of interacting online.
The pillars of Web3: technology and innovation
The driving forces behind Web3 include a range of advanced technologies.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning enable computers to process and understand information in a way that is similar to human intelligence.
In concrete terms, Web3 is based on these principles:
Decentralization: The heart of the matter
Web 3.0 marks the transition of the Internet from a centralized control structure to a decentralized network. Information is no longer stored on individual servers, but distributed across numerous locations based on its content. Through the use of open source software, every user is granted freedom and control over their data without the need for a central authority. This model creates a “trustless” and “permissionless” environment in which trust and permission no longer depend on traditional intermediaries.
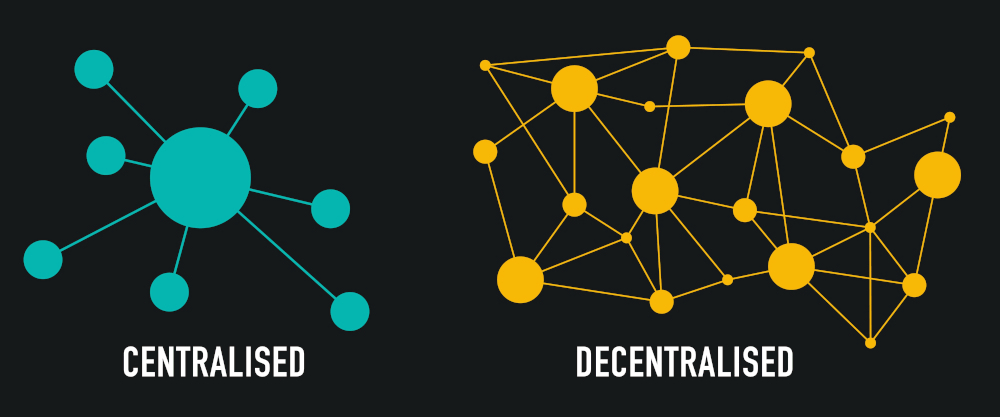
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies: The technological basis
Another core feature of Web 3.0 is the integration of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. These innovations enable distributed data management on a variety of computing resources – from smartphones to household appliances and vehicles. Blockchain ensures a permanent and unalterable record of all transactions, which increases authenticity and transparency and prevents attempts at manipulation. Blockchain thus forms the foundation for a robust, digital cryptocurrency system without central vulnerabilities.

Automation and artificial intelligence: efficiency and accuracy
The third pillar of Web 3.0 is the use of artificial intelligence (AI), which is supported by technologies such as predictive analytics and machine learning. Predictive analytics uses historical data and statistical models to predict future events or outcomes. These innovations make it possible to deliver relevant results faster and without human intervention. Automated processes and AI-powered analytics improve not only accuracy but also efficiency by operating free from external influences.

The potential of Web3
In theory, Web3 has the potential to improve the internet in many ways. It promises to give users more control over their data, increase privacy and reduce dependence on centralized platforms. This could lead to a fairer and more equitable digital economy in which creators and content producers are paid directly for their work without large middlemen siphoning off some of the profits.
However, despite its great potential, the development and acceptance of Web3 still faces a number of challenges. Issues of scalability, user-friendliness and regulation must be addressed in order to achieve broad acceptance.